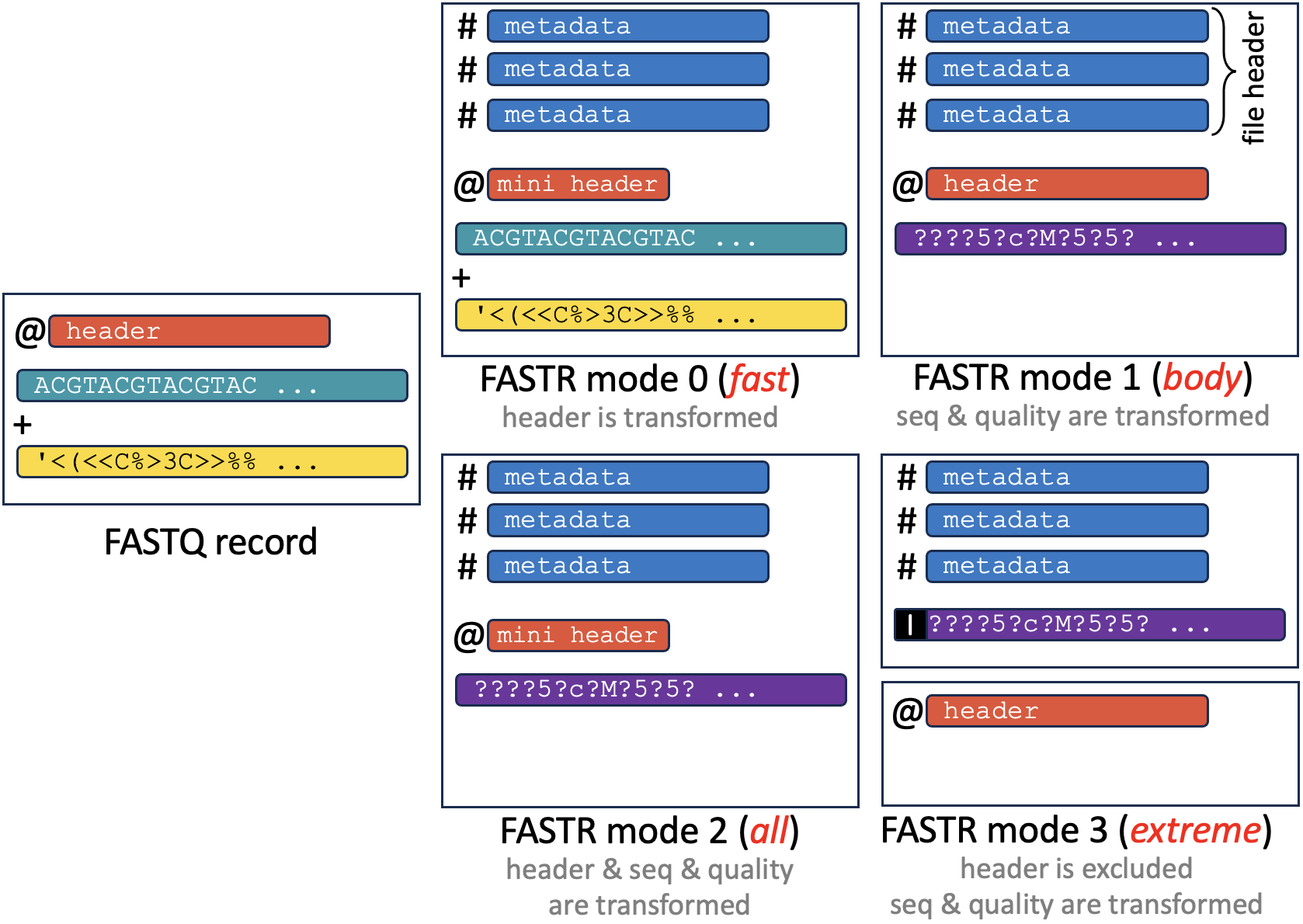
FASTR, an efficient file format designed for lossless storage of sequencing data as scalar (numerical) formats. FASTR transforms both textual DNA/RNA data (i.e., FASTQ) and their base quality scores into efficient/compact integer-based or binary representations.
- FASTR is at least 2x less in size than FASTQ, and hence better to read, process, transfer.
- FASTR can be further compressed using general-purpose compression tools, such as gzip, pigz, ...
- Extremely fast (multithreaded) and lossless FASTR-to-FASTQ & FASTQ-to-FASTR conversion.
- FASTR supports data from all prominent sequencing technologies (Illumina, ONT, PacBio's HiFi, and PacBio's CLR), single-end and paired-end reads, and SRA formats (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra).
- FASTR supports all widely-used Phred quality scores (Phred42, Phred63, Phred68Solexa, Phred94, Illumina RTA3, Illumina RTA4, and custom mathematical formulas).
- Flexible Output: binary (1 uint8 per FASTR value), integer (3 uint8s per FASTR value), with/without header.
- FASTR is compatible with minimap2 with no (or <2%) overhead, and with machine learning pipelines (i.e., numerical vectors).
Ensure you have Python 3.x installed. The tool relies on numpy and numba for efficient array handling.
git clone https://github.com/ALSER-Lab/FASTR.git
pip install -r requirements.txtusage: to_fastr.py [-h] [--mode INT] [--qual_scale STR] [--extract_qual INT]
[--phred_off INT] [--min_qual INT] [--custom_formula STR]
[--paired INT] [--paired_mode STR] [--seq_type STR]
[--compress_hdr INT] [--sra_acc STR] [--multi_flow INT]
[--rm_repeat_hdr INT] [--adaptive_sample INT]
[--mode3_headers STR] [--gray_N INT] [--gray_A INT]
[--gray_G INT] [--gray_C INT] [--gray_T INT]
[--bin_write INT] [--keep_bases INT] [--keep_qual INT]
[--phred_alpha STR] [--second_head INT] [--safe_mode INT]
[--workers INT] [--chunk_mb INT] [--profile INT]
[--verbose INT]
FILE FILE
Convert and compress FASTQ/FASTA files to FASTR format.
positional arguments:
FILE Path of .fastq file
FILE Output file path
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--mode3_headers STR Path to headers file for mode 3 reconstruction (read mode) [null]
OPERATION MODES:
--mode INT 0: Header compression only
1: Base conversion into numbers only
2: Header and base conversion, written out in two lines
3: Repeating header removal entirely, base conversion kept, written out in one line
QUALITY SCALING:
--qual_scale STR Quality scaling method. Available options: {'log', 'log_reverse', 'log_custom', 'one_hot', 'custom'} [one_hot]
--extract_qual INT For FASTQ: extract quality scores (0/1) [1]
--phred_off INT Phred quality offset [33]
--min_qual INT Clamped minimum quality score threshold [0]
--custom_formula STR Custom formula for quality scaling (use 'x' for quality score). Example: '1 + 62 * (x - 40) / 53' or 'ln(x) * 10'
PAIRED-END:
--paired INT Paired-end reads flag (0/1) [0]
--paired_mode STR Output mode for paired-end reads. Available options: {'same_file', 'separate_files'} [same_file]
SEQUENCER & HEADERS:
--seq_type STR Sequencer type for header compression. [adaptive]
Standard: {'illumina', 'pacbio_hifi', 'pacbio_clr', 'ont', 'sra', 'old_illumina'}
SRA Hybrid: {'illumina_sra', 'pacbio_hifi_sra', 'pacbio_clr_sra', 'ont_sra'}
--compress_hdr INT Compress FASTQ headers on-the-fly (0/1) [0]
--sra_acc STR SRA accession number (e.g., SRR12345678) [null]
--multi_flow INT Enable multiple flowcell detection and tracking (0/1) [0]
--rm_repeat_hdr INT Remove repeating metadata from headers, store only at top (0/1) [0]
--adaptive_sample INT
Number of headers to analyze for adaptive pattern detection [10]
ENCODING & GRAYSCALE:
--gray_N INT Grayscale value for N [0]
--gray_A INT Grayscale value for A [3]
--gray_G INT Grayscale value for G [66]
--gray_C INT Grayscale value for C [129]
--gray_T INT Grayscale value for T [192]
OUTPUT FORMAT:
--bin_write INT Enable binary writing of sequence integers (0/1) [1]
--keep_bases INT Return textual bases without scaling or one-hot encoding (0/1) [0]
--keep_qual INT Keep original quality scores in output (0/1) [0]
--phred_alpha STR Phred quality (q-score) ascii character alphabet used by input (phred42, phred63, phred94) [phred94]
--second_head INT Repeat the header on the '+' line in the FASTQ output.
--safe_mode INT Enable safe mode for modes 1 and 2 (adds 255 marker after headers) (0/1) [1]
PERFORMANCE & PARALLELIZATION:
--workers INT Number of parallel workers (use 4+ for large files >5GB) [1]
--chunk_mb INT Chunk size in MB for parallel processing [8]
--profile INT Enable profiling (0/1) [0]
--verbose INT Enable verbose logging (0/1) [0]python FASTR/src/to_fastr.py ERR15909551.fastq ERR15909551.fastr_mode0.fastr --mode 0 --qual_scale log --seq_type illumina_sra --workers 16 --phred_alpha phred94python FASTR/src/to_fastr.py ERR15909551.fastq ERR15909551.fastr_mode1.fastr --mode 1 --qual_scale log --seq_type illumina_sra --workers 16 --phred_alpha phred94python FASTR/src/to_fastr.py ERR15909551.fastq ERR15909551.fastr_mode2.fastr --mode 2 --qual_scale log --seq_type illumina_sra --workers 16 --phred_alpha phred94python FASTR/src/to_fastr.py ERR15909551.fastq ERR15909551.fastr_mode3.fastr --mode 3 --qual_scale log --seq_type illumina_sra --workers 16 --phred_alpha phred94usage: to_fastq.py [-h] [--mode INT] [--headers_file FILE]
[--phred_offset INT] [--phred_alphabet STR] [--gray_N INT]
[--gray_A INT] [--gray_G INT] [--gray_C INT] [--gray_T INT]
[--chunk_size_mb INT] [--num_workers INT] [--verbose INT]
[--profile INT]
FILE FILE
Reconstruct FASTQ files from FASTR.
positional arguments:
FILE Path to FASTR compressed file
FILE Output FASTQ file path
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
RECONSTRUCTION MODE:
--mode INT Reconstruction mode [2]
0: Headers only (no base conversion)
1: Bases only (keep original headers)
2: Full reconstruction (headers + bases)
3: No repeating headers (requires --headers_file)
--headers_file FILE Path to headers file for mode 3 reconstruction [null]
QUALITY RECONSTRUCTION:
--phred_offset INT Phred quality offset for output [33]
--phred_alphabet STR Override phred alphabet from metadata (phred42/phred63/phred94) [auto]
GRAYSCALE DECODING:
--gray_N INT Grayscale value for N [0]
--gray_A INT Grayscale value for A [3]
--gray_G INT Grayscale value for G [66]
--gray_C INT Grayscale value for C [129]
--gray_T INT Grayscale value for T [192]
PERFORMANCE & PARALLELIZATION:
--chunk_size_mb INT Chunk size in MB for parallel processing [8]
--num_workers INT Number of parallel workers [4]
--verbose INT Enable verbose logging (0/1) [0]
--profile INT Enable cProfile profiling (0/1) [0]python FASTR/src/to_fastq.py ERR15909551.fastr_mode0.fastr ERR15909551.fastr_mode0_decom.fastq --mode 0 --num_workers 16 --phred_alpha phred94python FASTR/src/to_fastq.py ERR15909551.fastr_mode1.fastr ERR15909551.fastr_mode1_decom.fastq --mode 1 --num_workers 16 --phred_alpha phred94python FASTR/src/to_fastq.py ERR15909551.fastr_mode2.fastr ERR15909551.fastr_mode2_decom.fastq --mode 2 --num_workers 16 --phred_alpha phred94python FASTR/src/to_fastq.py ERR15909551.fastr_mode3.fastr ERR15909551.fastr_mode3_decom.fastq --mode 3 --num_workers 16 --phred_alpha phred94 --headers_file ERR15909551.fastr_mode3_headers.txtIf you use FASTR in your work, please cite:
Adrian Tkachenko, Sepehr Salem, Ayotomiwa Ezekiel Adeniyi, Zulal Bingol, Mohammed Nayeem Uddin, Akshat Prasanna, Alexander Zelikovsky, Serghei Mangul, Can Alkan and Mohammed Alser. "FASTR: Reimagining FASTQ via Compact Image-inspired Representation" arXiv (2026). link.
Below is bibtex format for citation.